Welding revolution
A review of technological innovations in the welding industry.

The global market for welding gear is expected to reach over £12bln by 2026. With the constant evolution of technology and the development of construction and infrastructure, technological advancements in the welding industry can bring a wide range of benefits, transforming welding operations.
Among many other benefits, they can increase efficiency, reduce downtime, enhance safety, offer better precision and improve the quality of welding processes overall.
So, what are the latest, most innovative tools that are driving the sector forward?
More sectors are now using robots to facilitate their day-to-day operations. In more recent times, the welding industry has followed suit, adopting robots to ensure consistent quality, maximise productivity and facilitate cladding applications.
However, these ingenious tools have a high initial cost, both in terms of equipment investment and personnel training. But in the long run, they are likely to pay off the hefty expenses by largely increasing efficiency.
What’s more, another advantage of using robots in certain processes is that they can save staff from being exposed to hazardous fumes or radiation, and can significantly reduce the risk of repetitive strain injuries.
And for those operations where the supervision of human welders is necessary, there are collaborative welding robots (welding cobots) that can make the job easier. Equipped with sensors that allow them to work safely with humans without the need for barriers, cobots are designed to assist employees with the more repetitive, physically demanding aspects of welding.
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) welding simulators are also being used in the sector for training purposes. These high-tech headsets offer an immersive environment where workers can practice their skills in a safe and controlled manner.
In the case of VR, the equipment simulates a real-world, 360o scenario where the welder can carry out specific tasks. In AR, the welder uses a wearable device to access digital overlays that provide guidance and instructions as they perform an operation in real life.
The beauty of both is that they can offer instant feedback, helping welders nail their skills and identify areas that need further training. In turn, this can help both workers and companies improve production quality and minimise potential errors or defects.
Fitted with sensors, cameras and robotic arms, drones. meanwhile, are perfect for inspecting hard-to-reach or hazardous locations.
Regardless of a welder’s experience, performing processes on bridges, high-rise buildings, or offshore oil platforms can be dangerous. So, using drones can eliminate unnecessary risks or safety issues, as they can be operated remotely to check and adjust operations from a safe distance.
Since drones can access remote and hard-to-reach locations without much hassle, companies can save precious time and money. In fact, there will be no need for scaffolding, which can cause delay and impact finances.
One of the trickiest challenges for workers is to weld dissimilar metals. In some cases, it is borderline impossible.
In recent years, friction stir welding (FSW) has been introduced. This uses mechanical friction by applying pressure and rotating the metals at high speed, which, in turn, causes them to fuse and form a strong bond.
FSW is a particularly handy technique as it offers a clean, precise weld without any defects or porosity.
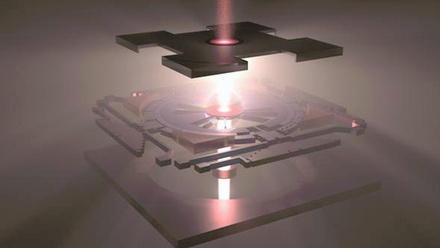
Similarly, laser beam welding (LBW) adopts a focused beam of light to melt and join different metals while keeping control over heat input and weld penetration. As well as guaranteeing precision and consistency, LBW can speed up what is usually a lengthy, time-consuming operation. Thanks to its reliability, this technology is increasingly being used in automotive, medical device and aerospace manufacturing.