Tata Steel announces CO2 savings
Improvements to furnaces see a decrease to its carbon footprint.
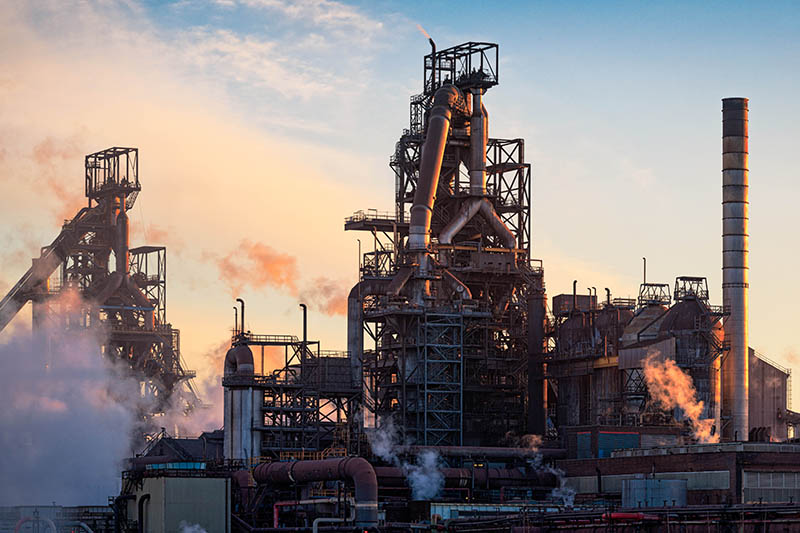

Tata Steel is improving the performance of the stoves at its Port Talbot Blast Furnaces
© Tata SteelThe two furnaces – located in Port Talbot, Wales – comprise of seven refractory-brick-lined stoves each around 45m high and 8m in diameter, and are powered by high pressure 'hot blast' air.
The improvements include recycling the gases in the furnaces in situ to keep the temperature greater than 1,100°C; upgrading the burners in three of the stoves; as well as replacing the refractory brick. Further work will be carried out concurrently with the remaining stoves being in use.
Speaking about the upgrades to the stoves, Project Manager Andrew McGregor says, 'Stoves are absolutely critical to the running of our blast furnaces. Any loss of efficiency in heating the air means we either have to use more gas than is optimum, or we have to replace that lost energy by using more metallurgical coke to chemically reduce the iron ore inside the furnaces'.
The programme of improvements is expected to reduce the site’s carbon footprint by about 160,000 tonnes of CO<sub>2</sub> a year. Andrew says, 'This programme of activity will make a significant difference to our carbon footprint, our energy costs and our operational stability and efficiency.'
A short video interview with Andrew about the improvements plays below.